Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Soma, Shu; Ishigaki, Masahiro*; Abe, Satoshi; Shibamoto, Yasuteru
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 10 Pages, 2024/00
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 4 Pages, 2022/06
We have developed a wind simulation code named CityLBM to realize wind digital twins. Mesoscale wind conditions are given as boundary conditions in CityLBM by using a nudging data assimilation method. It is found that conventional approaches with constant nudging coefficients fail to reproduce turbulent intensity in long time simulations, where atmospheric stability conditions change significantly. We propose a dynamic parameter optimization method for the nudging coefficient based on a particle filter. CityLBM was validated against plume dispersion experiments in the complex urban environment of Oklahoma City. The nudging coefficient was updated to reduce the error of the turbulent intensity between the simulation and the observation, and the atmospheric boundary layer was reproduced throughout the day.
Araki, Yasufumi; Watanabe, Jin*; Nomura, Kentaro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(9), p.094702_1 - 094702_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.57(Physics, Multidisciplinary)While nodal-line semimetals with magnetism have been theoretically predicted and experimentally observed in a few compounds, idea on the relation between the magnetic order and the electronic structure is still limited. We theoretically explore the electronic structure in bulk and boundary of such a magnetic nodal-line state by introducing magnetism in topological Dirac semimetal (TDSM). TDSMs, such as 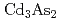 and
and 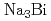 ,are characterized by a pair of spin-degenerate Dirac points protected by rotational symmetries of crystals. By introducing local magnetic moments coupled to the electron spins in the lattice model of TDSM, we show that the TDSM can turn into either a Weyl semimetal or a nodal-line semimetal, which is determined by the orbital dependence in the exchange coupling and the direction of magnetization formed by the magnetic moments. In this magnetic nodal-line semimetal state, we find zero modes with drumhead-like band structure at the boundary that are characterized by the topological number of
,are characterized by a pair of spin-degenerate Dirac points protected by rotational symmetries of crystals. By introducing local magnetic moments coupled to the electron spins in the lattice model of TDSM, we show that the TDSM can turn into either a Weyl semimetal or a nodal-line semimetal, which is determined by the orbital dependence in the exchange coupling and the direction of magnetization formed by the magnetic moments. In this magnetic nodal-line semimetal state, we find zero modes with drumhead-like band structure at the boundary that are characterized by the topological number of  . Those zero modes are numerically demonstrated by introducing magnetic domain walls in the lattice model.
. Those zero modes are numerically demonstrated by introducing magnetic domain walls in the lattice model.
Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Oka, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Satoshi; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Kaito, Takeji
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 9, p.353 - 359, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:64.88(Nuclear Science & Technology)Materials for core components of fusion reactors and fast reactors, such as blankets and fuel cladding tubes, must be excellent in high temperature strength and irradiation resistance because they will be exposed to high heat flux and heavy neutron irradiation. Oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steels have been developing as the candidate material. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have been developing 9 and 11 Chromium (Cr) ODS steels for advanced fast reactor cladding tubes. The JAEA 11Cr-ODS steels were rolled in order to evaluate their anisotropy. Tensile tests and creep tests of them were carried out at 700  C in longitudinal and transverse orientation. The anisotropy of tensile strength was negligible, though that of creep strength was distinct. The observation results and chemical composition analysis suggested that the cause of the anisotropy in creep strength was prior powder boundary including Ti-rich precipitates.
C in longitudinal and transverse orientation. The anisotropy of tensile strength was negligible, though that of creep strength was distinct. The observation results and chemical composition analysis suggested that the cause of the anisotropy in creep strength was prior powder boundary including Ti-rich precipitates.
Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Kukita, Yutaka*; Nakamura, Hideo
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 71(703), p.825 - 832, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Urano, Hajime
JAERI-Research 2004-027, 131 Pages, 2005/02
no abstracts in English
Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Kukita, Yutaka*; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Multiphase Flow (ICMF 2004) (CD-ROM), p.217_1 - 217_9, 2004/05
no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Sakurai, Shinji; Porter, G. D.*; Rognlien, T. D.*; Rensink, M. E.*; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Higashijima, Satoru; Kubo, Hirotaka
Nuclear Fusion, 44(4), p.503 - 512, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:89.68(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The measurements of the SOL flow and plasma profiles both at the high-field-side (HFS) and low-field-side (LFS), for the first time, found out the SOL flow pattern and its driving mechanism. "Flow reversal" was found near the HFS and LFS separatrix of the main plasma for the ion ▽B drift direction towards the divertor. Radial profiles of the SOL flow were similar to those calculated numerically using the UEDGE code with the plasma drifts included although Mach numbers in measurements were faster than those obtained numerically. Particle fluxes towards the HFS and LFS divertors produced by the parallel SOL flow and Er B drift flow were evaluated. The particle flux for the case of intense gas puff and divertor pump (puff and pump) was investigated, and it was found that both flow velocity and collisionality were enhanced, in particular, at HFS SOL. Drift flux in the private flux region was also evaluated, and important physics issues for the divertor design and operation, such as in-out asymmetries of the heat and particle fluxes, and control of impurity ions were investigated.
B drift flow were evaluated. The particle flux for the case of intense gas puff and divertor pump (puff and pump) was investigated, and it was found that both flow velocity and collisionality were enhanced, in particular, at HFS SOL. Drift flux in the private flux region was also evaluated, and important physics issues for the divertor design and operation, such as in-out asymmetries of the heat and particle fluxes, and control of impurity ions were investigated.
Ida, Mizuho*; Nakamura, Hideo; Nakamura, Hiroo; Takeuchi, Hiroshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 70(2), p.95 - 106, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 4 surface
4 surfaceTakahashi, Masamitsu; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Yamamoto, Naomasa*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Physical Review B, 68(8), p.085321_1 - 085321_5, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:62.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The  ,
,  and
and  phases of the GaAs(001)-2
phases of the GaAs(001)-2 4 surface have been investigated by
4 surface have been investigated by  surface X-ray diffraction in an As flux and at temperatures ranging from 480
surface X-ray diffraction in an As flux and at temperatures ranging from 480 C to 610
C to 610 C. It has been found that the fractional-order peaks originating from the fourfold symmetry show shift in the [110] direction as well as significant broadening of the peaks in the
C. It has been found that the fractional-order peaks originating from the fourfold symmetry show shift in the [110] direction as well as significant broadening of the peaks in the  and
and  phases. The direction of the peak shift is characteristic in each phase. This behavior is explained by the formation of the antiphase domain boundaries. The atomic structure of the domain boundaries is discussed.
phases. The direction of the peak shift is characteristic in each phase. This behavior is explained by the formation of the antiphase domain boundaries. The atomic structure of the domain boundaries is discussed.
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Sakurai, Shinji; Itami, Kiyoshi; Naito, Osamu; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Higashijima, Satoru; Koide, Yoshihiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Kubo, Hirotaka; Porter, G. D.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316, p.820 - 827, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:89.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Nakano, Tomohide; Higashijima, Satoru; Kubo, Hirotaka; Takenaga, Hidenobu
Proceedings of 30th EPS Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2003/00
The measurements of the parallel SOL flow (Mach number, M) and electric field (Er) both at the high-field-side (HFS) and low-field-side (LFS) have been accomplished using Mach probes in JT-60U. Particle fluxes towards the HFS and LFS divertors produced by the parallel SOL flow (niMCs) and ErxB drift flow (niEr/B) were evaluated. For the case of intense gas puffing from the plasma top (puff and pump), Zeff was reduced largely to 1.3, comparing to 1.42 for the divertor gas puff. It was found that both M and ni in niMCs were enhanced, in particular, at HFS. On the other hand, niEr/B for the two cases were comparable since ni increased and Er decreased for the puff and pump. Friction force and thermal force on impurity ions were estimated from the measured M, ne, Te and Ti, and ratios of Ffric/Fi-therm at HFS increased to 3-4 compared to 1.5-1.8 for the divertor gas puff. This result was consistent with a conventional model of reduction in Zeff. Two-dimensional transport of the carbon impurity at the HFS and LFS divertors was discussed using IMPMC (Impurity Monte-Carlo) code.
Chankin, A. V.; Stangeby, P. C.*
Proceedings of 30th EPS Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2003/00
no abstracts in English
Utsumi, Takayuki*; Koga, J. K.
Computer Physics Communications, 148(3), p.281 - 290, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.15(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Sakurai, Shinji; Sakasai, Akira; Tamai, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Porter, G. D.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 44(10), p.2101 - 2119, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:54.51(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Sakurai, Shinji; Naito, Osamu; Itami, Kiyoshi; Miura, Yukitoshi; Higashijima, Satoru; Koide, Yoshihiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 44(5A), p.A313 - A321, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:57.23(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Fujita, Takaaki
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 44(5A), p.A19 - A35, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:63.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Satoru; Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8410 2001-028, 36 Pages, 2002/03
For a safety assessment of the high-level radioactive waste disposal, effective diffusion coefficients (D ) of radionuclides in bentonite have been accumulated by the through-diffusion method. It has been found recently that experimental results on D
) of radionuclides in bentonite have been accumulated by the through-diffusion method. It has been found recently that experimental results on D s for several cations (cesium and strontium) by the fairly standard experimental method in JNC differ from those previously reported in several papers. Discrepancy can be considered to be due to different design of diffusion cell and system. In order to confirm influences of the experimental design on cation diffusivities in bentonite, a flow-through diffusion system was developed and several diffusion experiments were conducted.As a result, magnitude of D
s for several cations (cesium and strontium) by the fairly standard experimental method in JNC differ from those previously reported in several papers. Discrepancy can be considered to be due to different design of diffusion cell and system. In order to confirm influences of the experimental design on cation diffusivities in bentonite, a flow-through diffusion system was developed and several diffusion experiments were conducted.As a result, magnitude of D and its salinity dependence were relatively different between the standard and flow-through diffusion system. Since the latter system can control boundary conditions of the experiment more strictly than the standard method, we can conclude that the flow-through diffusion system provide correct results. In addition, we apply this flow-through diffusion system to a modification of controlling boundary condition during the experiment and to the diffusion experiment under controlled temperature.
and its salinity dependence were relatively different between the standard and flow-through diffusion system. Since the latter system can control boundary conditions of the experiment more strictly than the standard method, we can conclude that the flow-through diffusion system provide correct results. In addition, we apply this flow-through diffusion system to a modification of controlling boundary condition during the experiment and to the diffusion experiment under controlled temperature.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Fukuda, Takeshi; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; Takizuka, Tomonori; Itami, Kiyoshi; Fujita, Takaaki; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 42(6), p.637 - 642, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Loarte, A.*; Porter, G.*; Philipps, V.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Kallenbach, A.*; Matthews, G.*; Federici, G.*; Kukushkin, A.*; Mahdavi, A.*; et al.
IAEA-CN-94/CT/P-01, 5 Pages, 2002/00
Three important physics issues for the ITER divertor design and operation are summarized based on the experimental and numerical work from multi-machine database (JET, JT-60U, ASDEX Upgrade, DIII-D, Alcator C-Mod and TEXTOR). (i) The energy load associated with Type-I ELMs is of great concern for the lifetime of the ITER divertor target. In order to understand the physics base of the scaling models, the ELM heat and particle transport to the divertor is investigated. Convective transport during ELMs plays an important role in heat transport to the divertor. (ii) Determination of the SOL flow pattern and the driving mechanism has progressed experimentally and numerically. Influences of the drift effects on the SOL and divertor plasma transport were discussed. (iii) Characteristics of chemical yield at two different deposited carbon surfaces, i.e. erosion- and redeposition-dominated areas, have been studied. Progress of understanding the chemical erosion is reviewed.